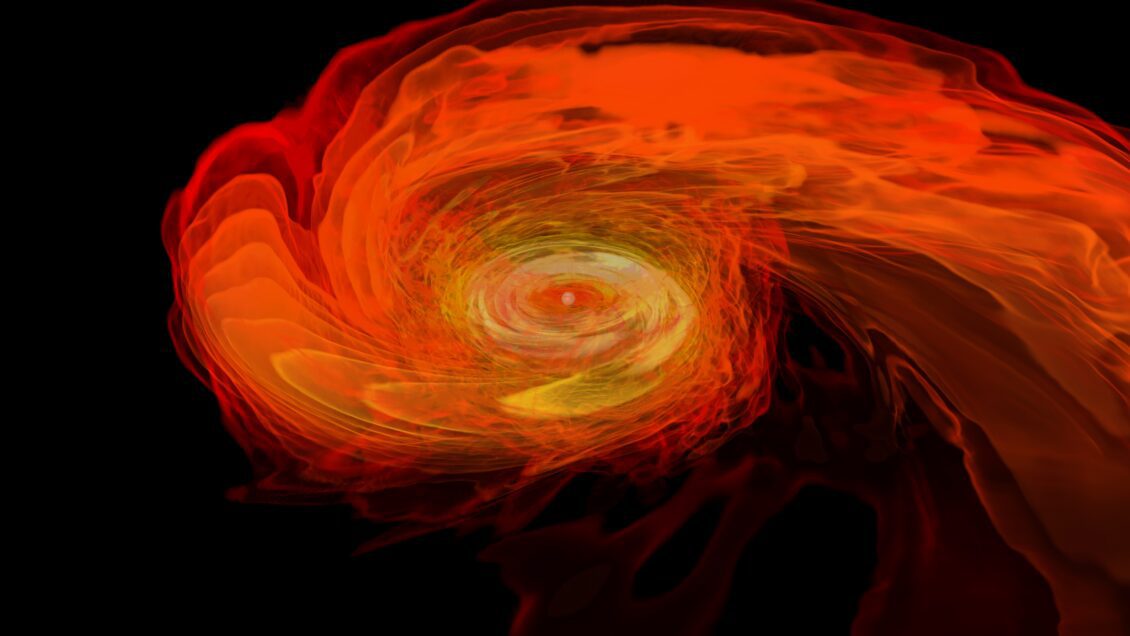
Dieter Hartmann and an international team of astronomers “obtained observational evidence for the creation of rare heavy elements in the aftermath of a cataclysmic explosion triggered by the merger of two neutron stars.” They were studying a massive gamma-ray burst named GRB230307A, which was first detected on March 7, 2023. Scientists discovered that this burst resulted from two neutron stars merging in a distant galaxy.
“The breakthrough discovery puts astronomers one step closer to solving the mystery of the origin of elements that are heavier than iron.”
Adapted from:
Astronomers discover heavy elements after bright gamma-ray burst from neutron star merger | Clemson News